Experiment management¶
In lumo, theExperimentclass provides sufficient guarantees to ensure experiment reproducibility. Specifically,Experimentguarantees reproducibility from four perspectives: path management, version control, parameter recording, and backup. It also simplifies the operation threshold through visual panels, command-line interfaces, and other methods.
Path Management¶
To ensure that paths are not duplicated,Experimentassigns a unique experiment ID (test_name) to each experiment run. At the same time,Experimentprovides three different types of data storage paths for storing information (info_dir), binary files (blob_dir), and temporary files (cache_dir), with the following path relationships:
- <cache_root>
- <exp_name>
- <cache_dir>
- <info_root>
- <exp_name>
- <info_dir>
- <blob_root>
- <exp_name>
- <blob_dir>
Version Control¶
The lifecycle ofExperimentincludes start/progress/end, and a series ofExpHookclasses are set up to perform partial operations at each lifecycle stage. Among them,~lumo.exp.exphook.GitCommitis responsible for git commit, which checks for file changes aton_startand submits a snapshot of the current file to thelumo_experimentsbranch if changes exist. The commit information corresponding to the current code is recorded in theinfo_dirof theExperimentinstance and can be viewed throughexp.properties['git'].
Information Recording¶
Information recording includes startup parameters such as hyperparameters and program execution parameters, runtime and post-run parameters such as Metric, execution time, and other metadata. All information mentioned except for hyperparameters is automatically recorded byExperimentat.start(). The hyperparameters of the experiment can be recorded byexp.dump_info('params', params_dict).
When using
lumo.Trainerfor training, hyperparameters used are automatically recorded in theparamskey.
For Metric, theExperimentinstance can be recorded using.dump_metricand.dump_metrics(), for example:
max_acc = exp.dump_metric("acc",acc, "cls_acc", cls_acc)
Here shows an example in exp.properties
{'agent': nan,
'backup': {'23-03-17-161847': {'backend': 'github',
'number': 4,
'repo': 'sailist/image-classification'}},
'deprecated': nan,
'exception': nan,
'execute': {'cwd': '~/python/image-classification-private',
'exec_argv': ['train_ssl.py',
'train_ssl.py',
'--module=simclr',
'--device=2',
'--config=config/ssl/simclr/cifar100.yaml',
'--model=wrn282',
'--scan=ssl-2023.02.28'],
'exec_bin': '~/miniconda3/bin/python3',
'exec_file': 'train_ssl.py',
'repo': '~/python/image-classification-private'},
'exp_name': 'simclr.simclrexp',
'git': {'commit': '294ccdac',
'dep_hash': '404fc6044b2119d56a5e8b92ac02fc1c',
'repo': '~/python/image-classification-private'},
'hooks': {'Diary': {'loaded': True, 'msg': ''},
'FinalReport': {'loaded': True, 'msg': ''},
'GitCommit': {'loaded': True, 'msg': ''},
'LastCmd': {'loaded': True, 'msg': ''},
'LockFile': {'loaded': True, 'msg': ''},
'RecordAbort': {'loaded': True, 'msg': ''}},
'lock': {'accelerate': '0.16.0',
'decorator': '5.1.1',
'fire': '0.5.0',
'hydra': '1.3.1',
'joblib': '1.2.0',
'lumo': '0.15.0',
'numpy': '1.24.2',
'omegaconf': '2.3.0',
'psutil': '5.9.4',
'torch': '1.8.1+cu101',
'torch.version.cuda': '10.1'},
'note': '',
'params': {'apply_mixco': False,
'apply_unmix': False,
'config': 'config/ssl/simclr/cifar100.yaml',
'dataset': 'cifar100',
'detach_cls': True,
'device': 2,
'ema': True,
'ema_alpha': 0.99,
'epoch': 1000,
'eval': {'batch_size': 512,
'num_workers': 8,
'pin_memory': True,
'shuffle': True},
'feature_dim': 128,
'hidden_feature_size': 128,
'knn': True,
'knn_k': 200,
'knn_t': 0.1,
'linear_eval': False,
'lr_decay_end': 0.0005,
'method': 'simclr',
'model': 'wrn282',
'module': 'simclr',
'more_sample': True,
'n_classes': 100,
'optim': {'lr': 0.06,
'momentum': 0.9,
'name': 'SGD',
'weight_decay': 0.0005},
'pretrain_path': None,
'scan': 'ssl-2023.02.28',
'seed': 1,
'semi_eval': False,
'stl10_unlabeled': True,
'temperature': 0.1,
'test': {'batch_size': 512,
'num_workers': 8,
'pin_memory': True,
'shuffle': False},
'train': {'batch_size': 512,
'num_workers': 8,
'pin_memory': True,
'shuffle': True},
'train_ending': 10,
'train_linear': True,
'train_strategy': 'ending',
'warmup_epochs': 0,
'warmup_from': 0.01,
'with_bn': False},
'pinfo': {'hash': '62ee6de98b381872e200e82901ad51f7',
'obj': {'argv': ['~/miniconda3/bin/python3',
'train_ssl.py',
'train_ssl.py',
'--module=simclr',
'--device=2',
'--config=config/ssl/simclr/cifar100.yaml',
'--model=wrn282',
'--scan=ssl-2023.02.28'],
'pid': 27687,
'pname': 'python3',
'pstart': 1678763482.5},
'pid': 27687},
'progress': {'finished': False,
'last_edit_time': '23-03-14-212932',
'ratio': 1.0,
'start': '23-03-14-111124',
'update_from': None},
'rerun': {'from': '230313.015.99t', 'repeat': 1},
'test_name': '230314.000.a3t',
...
}
Retrieve Experiment¶
Watchconsolidates information for all experiments, allowing users to search for a specific experiment.
from lumo import Watcher, Experiment
w = Watcher()
df = w.load() # all experiments
exp = Experiment.from_cache(df.iloc[0].to_dict())
For a known experiment withtest_name, theExperimentinstance can be directly retrieved using theretrievemethod:
w.retrieve('230306.012.d5t')
>>> Experiment(info_dir=".../.lumo/experiments/moco.mocoexp/230306.012.d5t")
Visual Panel¶
A fixed-style panel can never satisfy everyone’s needs. Therefore, lumo provides dynamic panels based on pandas and panel, with all styles except for a few fixed parts added by the user:
from lumo import Watcher
w = Watcher()
df = w.load()
... filter operations ...
new_df = ...
w.panel(new_df)
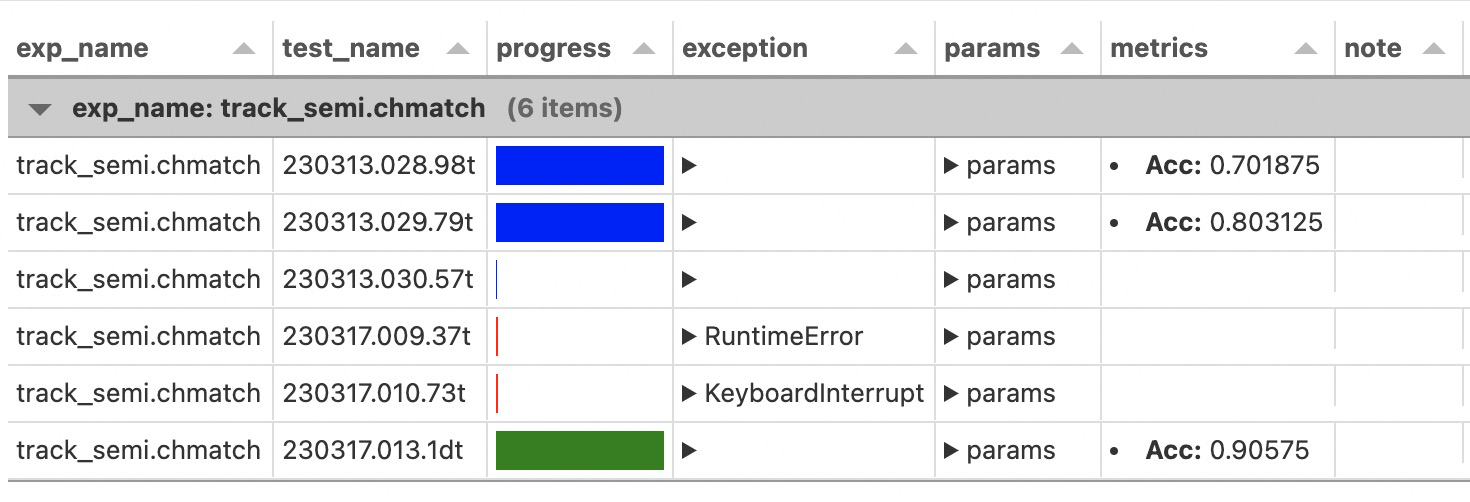
Repetitive Experiment¶
Repetitive experiments mainly occur in two scenarios:
To verify the stability of the results, rerun the experiment with other random seeds and the same parameters.
In the middle of the experiment, due to memory, disk space, or other reasons, the experiment failed and needs to be rerun with similar parameters.
Especially when scanning parameters, if only